Introduction
Structured Query Language (SQL) enables developers to interact with databases, perform queries, update data, and manage database structures efficiently. The ubiquity of data-driven decision-making in business today elevates the importance of SQL skills, making them indispensable for software developers across various industries.
According to Statista, SQL is the 2nd most popular database management system worldwide. This widespread adoption shows its critical role in data manipulation, analysis, and management, making SQL skills essential for many development roles.
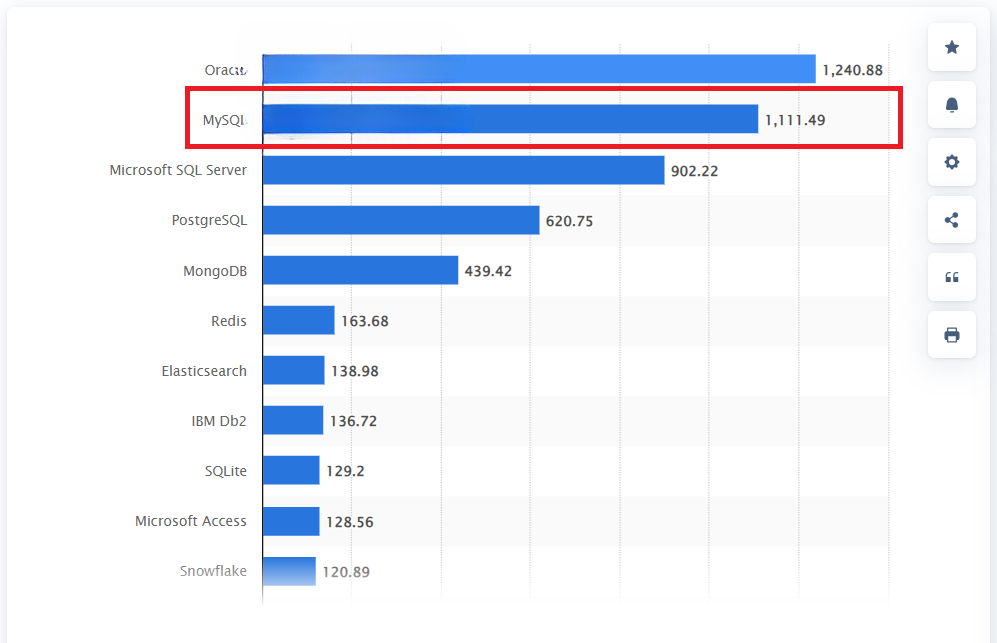
In this article, we aim to equip hiring managers and technical recruiters with a toolkit of essential SQL interview questions. These questions are designed to uncover a candidate’s theoretical understanding of SQL and their practical experience and problem-solving abilities.
What is SQL?
SQL, which stands for Structured Query Language, is a domain-specific language used in programming and designed for managing data held in a relational database management system (RDBMS) or for stream processing in a relational data stream management system (RDSMS).
It is particularly effective for inserting, querying, updating, and deleting data, as well as for managing database schemas and controlling access to data. SQL provides a standardized way for developers and database administrators to interact with the database in a readable and straightforward manner.
According to the TIOBE Index, SQL is ranked as the 7th most popular programming language in 2024. This ranking highlights SQL’s enduring relevance and widespread use in software development, database management, and data analysis fields.
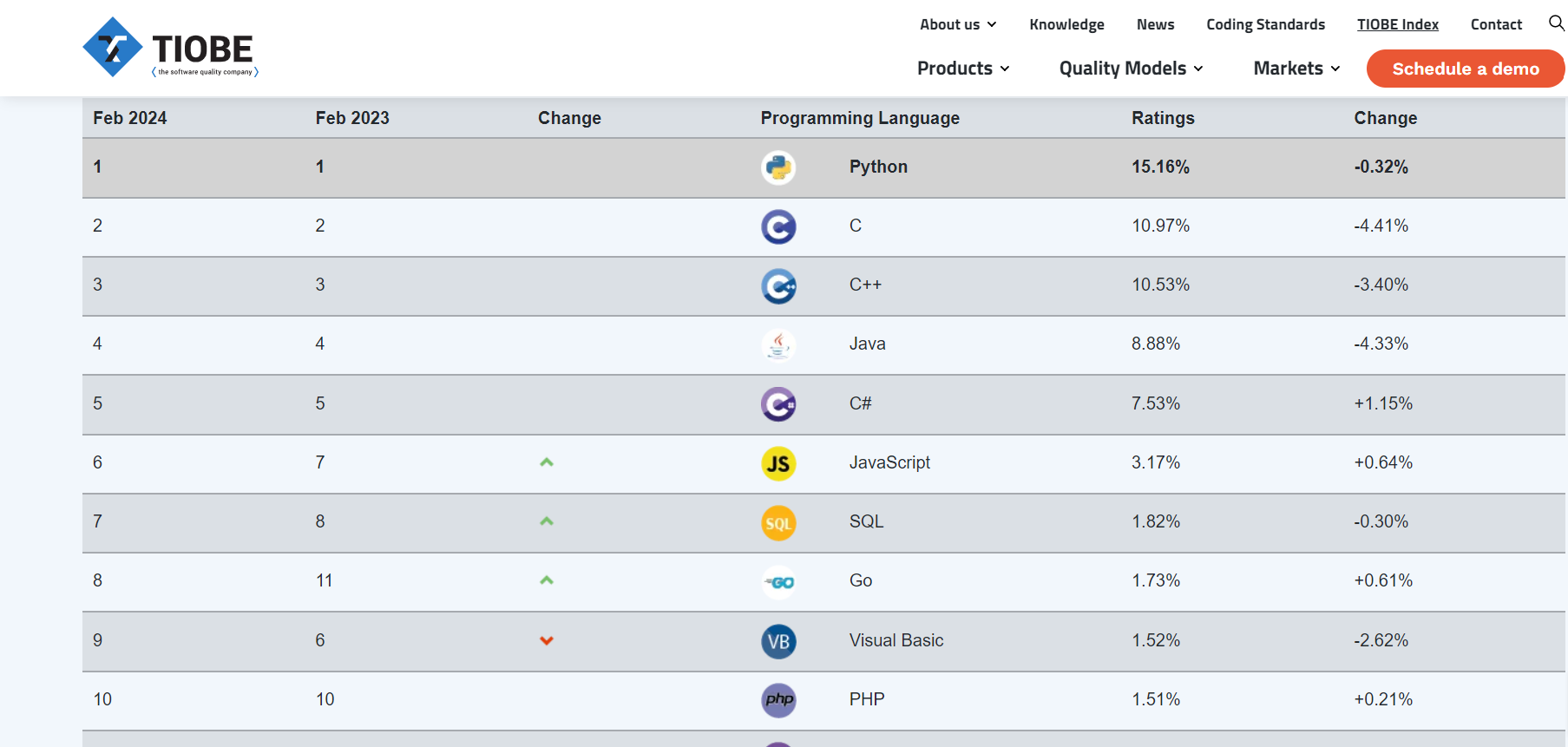
History
The development of SQL dates back to the early 1970s at IBM, where it was initially part of a project aimed at creating a system that could efficiently store and retrieve large amounts of data. The language, originally called SEQUEL (Structured English Query Language), was designed to manipulate and retrieve data stored in IBM’s original quasi-relational database management system.
The name was later changed to SQL due to trademark issues. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) have standardized SQL since 1986 and 1987, respectively, ensuring that it remains universally accessible and consistently implemented across different database systems.
Key Features
- Flexibility and Wide Adoption: SQL is used by a wide range of database systems, from commercial products like Microsoft SQL Server and Oracle Database to open-source systems like PostgreSQL and MySQL. This wide adoption makes SQL skills highly transferable between different platforms and systems.
- Powerful Data Manipulation Capabilities: SQL excels at data manipulation, allowing users to query, insert, update, and delete data within a database effortlessly.
- Complex Query Support: SQL supports complex queries that can retrieve data from multiple tables in a single command, making it a powerful tool for data analysis and reporting.
- Transaction Control: SQL provides mechanisms for transaction control, which help ensure data integrity by allowing multiple database operations to be executed as a single unit of work.
- Security Features: It includes features for controlling access to data at a granular level, including permissions and roles that restrict unauthorized data access.
SQL Examples
- Querying Data: To select data from a table named employees, you would use the following SQL statement:
| SELECT * FROM employees; |
- Inserting Data: To insert a new record into the employees table:
| INSERT INTO employees (name, position, department) VALUES (‘Jane Doe’, ‘Software Engineer’, ‘Development’); |
- Updating Data: To update an existing record in the employees table:
| UPDATE employees SET department = ‘Product Development’ WHERE name = ‘Jane Doe’; |
- Deleting Data: To delete a record from the employees table:
| DELETE FROM employees WHERE name = ‘Jane Doe’; |
Popular Companies Using SQL
Many leading companies across various industries rely on SQL to manage their databases, analyze data, and support their software applications. According to Zipdo, SQL Server has over 32,000 companies as customers. This shows the SQL Server’s widespread adoption versatility, and reliability as a database management system across diverse sectors.
Here’s a list of popular companies known for using SQL:
- Google: Uses SQL for various data manipulation and analysis tasks across its products and services.
- Amazon: Employs SQL to manage its vast e-commerce database, including customer information, order tracking, and inventory management.
- Facebook: Utilizes SQL to query and analyze vast amounts of social media data, including user interactions and engagement metrics.
- Microsoft: Beyond developing Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft uses SQL extensively across its product lines, including its cloud services and internal data analytics.
- IBM: As pioneers in the development of relational database systems, IBM uses SQL across its many software and analytics offerings.
- Apple: Relies on SQL for managing data across its various services, including the App Store, Apple Music, and iCloud.
- Netflix: Uses SQL for analyzing viewer data to make content recommendations and understand viewing patterns.
- LinkedIn: Employs SQL to manage user data, job postings, and professional network interactions.
- Uber: Utilizes SQL to manage ride data, user accounts, and pricing information in real-time.
- Twitter: Relies on SQL to analyze tweet data, user interactions, and trending topics.
10 Must Ask SQL Interview Questions
Let’s explore the top 10 SQL interview questions:
1. Write a SQL query to find the second highest salary from the employees table
| Task | The task is to write a SQL query that selects the second highest salary from a table named employees. |
| Input Format | The employees table is structured as follows:
|
| Constraints |
|
| Output Format | The output should be a single number (the second highest salary). |
Sample Input
| id | name | salary |
| 1 | John Doe | 50000 |
| 2 | Jane Smith | 60000 |
| 3 | Bob Davis | 55000 |
Sample Output
| 55000 |
Suggested Answer
| SELECT MAX(salary) AS SecondHighestSalary
FROM employees WHERE salary < (SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees); |
Code Explanation
This query works by first finding the highest salary in the employees table using a subquery (SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees) and then using this result to find the maximum salary that is less than the highest salary, effectively giving us the second highest salary.
| Common Mistakes to Watch Out For |
|
| Follow-ups |
|
| What the Question Tests? | This question assesses the candidate’s understanding of subqueries, aggregate functions, and their ability to think through complex SQL query requirements. It also tests the candidate’s knowledge of SQL syntax and their ability to manipulate data to meet specific conditions. |
2. Write a SQL query to list all employees and their managers
| Task | The goal is to write a SQL query that lists all employees along with their managers from an employees table, assuming the table includes both employee data and a reference to their manager in the same table. |
| Input Format | The employees table is structured as follows:
|
| Constraints |
|
| Output Format | The output should be a list of employee names along with their manager’s names. |
Sample Input
| id | name | manager_id |
| 1 | Alice King | NULL |
| 2 | Bob Marsh | 1 |
| 3 | Charlie Sheen | 1 |
Sample Ouput
| Employee | Manager Name |
| Bob Marsh | Alice King |
| Charlie Sheen | Alice King |
Suggested Answer
| SELECT
e.name AS EmployeeName, m.name AS ManagerName FROM employees e LEFT JOIN employees m ON e.manager_id = m.id; |
Code Explanation
This query performs a left join on the employees table itself, aliasing it as e for employees and m for managers based on the manager_id column. The LEFT JOIN ensures that all employees are listed, including those without a manager.
| Common Mistakes to Watch Out For |
|
| Follow-ups |
|
| What the Question Tests? | This question evaluates the candidate’s understanding of SQL joins, specifically the ability to self-join a table to relate rows within the same table based on a hierarchical relationship. It tests the candidate’s ability to visualize and manipulate table relationships and their skill in presenting relational data in a readable format. |
3. Write a SQL query to find the average salary within each department
| Task | Create a SQL query to calculate the average salary for each department in a company’s database, grouping the results by department. |
| Input Format | The database includes a table named departments and another table named employees. The structure for these tables is as follows:
|
| Constraints |
|
| Output Format | The output should list each department’s name along with the average salary of its employees. |
Sample Input
departments table:
| department_id | department_name |
| 1 | Engineering |
| 2 | Sales |
employees table:
| id | name | salary | department_id |
| 1 | John Doe | 70000 | 1 |
| 2 | Jane Smith | 80000 | 1 |
| 3 | Bob Brown | 60000 | 2 |
Sample Ouput
| Deparment Name | Average Salary |
| Engineering | 75000 |
| Sales | 60000 |
Suggested Answer
| SELECT
d.department_name, AVG(e.salary) AS AverageSalary FROM employees e JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id GROUP BY d.department_name; |
Code Explanation
This query joins the employees table with the departments table to correlate each employee with their respective department. It then groups the results by department name and calculates the average salary for each group, showcasing the use of the AVG aggregate function along with GROUP BY.
| Common Mistakes to Watch Out For |
|
| Follow-ups |
|
| What the Question Tests? | This question assesses the candidate’s ability to use aggregate functions (AVG in this case) and their understanding of how to join tables and group results to provide meaningful insights into the data. It tests knowledge of SQL syntax and the ability to interpret and manipulate relational data effectively. |
4. Write a SQL query to identify employees who have never been assigned a project
| Task | The task is to create a SQL query that identifies employees from the employees table who do not have any records in the projects table, indicating they have never been assigned a project. |
| Input Format | The relevant tables and their structures are as follows:
|
| Constraints |
|
| Output Format | The output should be a list of names of employees who have never been assigned a project. |
Sample Input
employees table:
| employee_id | name |
| 1 | Alice Johnson |
| 2 | Bob Smith |
| 3 | Charlie Smith |
projects table:
| project_id | project_name | employee_id |
| 1 | Project A | 1 |
| 2 | Project B | 1 |
| 3 | Project C | 2 |
Sample Ouput
| Name |
| Charlie Smith |
Suggested Answer
| SELECT e.name
FROM employees e LEFT JOIN projects p ON e.employee_id = p.employee_id WHERE p.project_id IS NULL; |
Code Explanation
This query uses a LEFT JOIN to connect the employees table with the projects table based on the employee_id. It then filters the results to include only those records where there is no corresponding project_id in the projects table, which means those employees have not been assigned to any projects.
| Common Mistakes to Watch Out For |
|
| Follow-ups |
|
| What the Question Tests? | This question tests the candidate’s understanding of SQL JOIN operations, particularly the use of LEFT JOIN to identify missing relationships between two tables. It evaluates the ability to accurately filter data based on the absence of related records, showcasing skills in data analysis and manipulation for specific conditions. |
5. Write a SQL query to retrieve the top 3 most expensive products in each category
| Task | The goal is to craft a SQL query that fetches the top 3 most expensive products within each product category from a products table. |
| Input Format | The structure for the products table is as follows:
|
| Constraints |
|
| Output Format | The output should list the category_id along with product_name and price for the top 3 most expensive products in each category, ordered by category_id and then by price in descending order. |
Sample Input
products table:
| product_id | product_name | price | category_id |
| 1 | Product A | 100 | 1 |
| 2 | Product B | 150 | 1 |
| 3 | Product C | 120 | 1 |
| 4 | Product D | 200 | 2 |
| 5 | Product E | 180 | 2 |
| 6 | Product F | 220 | 2 |
Sample Output
| category_id | product_name | price |
| 1 | Product B | 150 |
| 1 | Product C | 120 |
| 1 | Product A | 100 |
| 2 | Product F | 220 |
| 2 | Product D | 200 |
| 2 | Product E | 180 |
Suggested Answer
| SELECT category_id, product_name, price
FROM ( SELECT category_id, product_name, price, RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY category_id ORDER BY price DESC) as price_rank FROM products ) as ranked_products WHERE price_rank <= 3 ORDER BY category_id, price DESC; |
Code Explanation
This query employs a window function (RANK()) to assign a rank to each product based on its price within its respective category (PARTITION BY category_id). It orders the products by price in descending order within each category.
By using a subquery, it filters these ranked products to include only those with a price_rank of 3 or less, effectively retrieving the top 3 most expensive products in each category.
| Common Mistakes to Watch Out For |
|
| Follow-ups |
|
| What the Question Tests? | This question tests the candidate’s ability to utilize advanced SQL features like window functions for complex data analysis tasks. It assesses understanding of how to partition data for analysis, rank results within these partitions, and filter data based on these rankings. |
6. Write a SQL query to find all duplicate names in the employees table
| Task | The task is to write a SQL query that identifies all names in the employees table that appear more than once, indicating duplicate entries based on the name. |
| Input Format | The employees table structure is as follows:
|
| Constraints |
|
| Output Format | The output should be a list of duplicate names from the employees table. |
Sample Input
employees table:
| employee_id | name |
| 1 | John Doe |
| 2 | Jane Smith |
| 3 | John Doe |
Sample Output
| name |
| John Doe |
Suggested Answer
| SELECT name
FROM employees GROUP BY name HAVING COUNT(name) > 1; |
Code Explanation
This query groups the records in the employees table by the name column and uses the HAVING clause to filter out the groups that have a count greater than 1. This effectively identifies names that appear more than once in the table, indicating duplicates.
| Common Mistakes to Watch Out For |
|
| Follow-ups |
|
| What the Question Tests? | This question tests the candidate’s ability to perform basic data aggregation and filtering with SQL. It evaluates understanding of the GROUP BY and HAVING clauses for identifying duplicate entries in a dataset. |
7. Write a SQL query to list all employees who joined after the average joining date of their department
| Task | Your goal is to write a SQL query that identifies employees from the employees table who have joined their respective departments after the average joining date of all employees in that department. |
| Input Format | The database includes two tables, structured as follows:
|
| Constraints |
|
| Output Format | The output should be a list of employee names who joined their department after the average joining date of that department, along with their join date and department name. |
Sample Input
departments table:
| department_id | department_name |
| 1 | Engineering |
| 2 | Marketing |
employees table:
| employee_id | name | join_date | department_id |
| 1 | John Doe | 2020-01-10 | 1 |
| 2 | Jane Smith | 2021-03-15 | 1 |
| 3 | Bob Brown | 2022-07-22 | 2 |
Sample Output
| Name | Join Date | Department Name |
| Jane Smith | 2021-03-15 | Engineering |
Suggested Answer
| SELECT
e.name, e.join_date, d.department_name FROM employees e INNER JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id WHERE e.join_date > (SELECT AVG(e2.join_date) FROM employees e2 WHERE e2.department_id = e.department_id); |
Code Explanation
This query first calculates the average joining date for each department by using a subquery that groups employees by their department and computes the average of their joining dates.
Then, it filters out employees whose joining date is greater than this average, indicating they joined after the average joining date for their department. An inner join with the departments table ensures that the department name is included in the output.
| Common Mistakes to Watch Out For |
|
| Follow-ups |
|
| What the Question Tests? | This question assesses the candidate’s ability to use subqueries effectively, particularly for computing aggregate functions within specific partitions of data (in this case, departments). |
8. Write a SQL query to find the department with the highest number of employees
| Task | Your objective is to write a SQL query that identifies the department from the departments table with the highest number of employees. |
| Input Format | The relevant tables and their structures are as follows:
|
| Constraints |
|
| Output Format | The output should be the name of the department with the highest number of employees. |
Sample Input
departments table:
| department_id | department_name |
| 1 | Engineering |
| 2 | Marketing |
employees table:
| employee_id | name | department_id |
| 1 | John Doe | 1 |
| 2 | Jane Smith | 1 |
| 3 | Bob Brown | 2 |
| 4 | Alice Blue | 1 |
Sample Output
| Name |
| Engineering |
Suggested Answer
| SELECT d.department_name
FROM departments d JOIN employees e ON d.department_id = e.department_id GROUP BY d.department_name ORDER BY COUNT(e.employee_id) DESC LIMIT 1; |
Code Explanation
This query joins the departments and employees tables to associate each employee with their respective department. It then groups the results by department name and orders them by the count of employees in each department in descending order.
By using LIMIT 1, the query selects the top result, which corresponds to the department with the highest number of employees.
| Common Mistakes to Watch Out For |
|
| Follow-ups |
|
| What the Question Tests? | This question evaluates the candidate’s ability to perform SQL aggregate functions (COUNT in this case) combined with GROUP BY to organize data based on specific criteria (department names). It tests the candidate’s understanding of how to sort aggregated results (ORDER BY) and select a specific number of top results (LIMIT). |
9. Write a SQL query to calculate the total sales for each salesman who has made more than three sales, including the salesman’s name and total sales amount
| Task | Create a SQL query that calculates the total sales amount for each salesman in the sales table who has made more than three sales. The output should include the salesman’s name and the total sales amount. |
| Input Format | The structure for the sales table is as follows:
|
| Constraints |
|
| Output Format | The output should list the name of each salesman who has made more than three sales, along with their total sales amount. |
Sample Input
sales table:
| sale_id | saleman_name | sale_amount | sale_date |
| 1 | John Doe | 100 | 2022-01-01 |
| 2 | Jane Smith | 200 | 2022-01-02 |
| 3 | John Doe | 150 | 2022-01-03 |
| 4 | Jane Smith | 250 | 2022-01-04 |
| 5 | John Doe | 300 | 2022-01-05 |
| 6 | John Doe | 50 | 2022-01-06 |
Sample Output
| Salemane Name | Total Sale Amount |
| John Doe | 600 |
Suggested Answer
| SELECT salesman_name, SUM(sale_amount) AS TotalSalesAmount
FROM sales GROUP BY salesman_name HAVING COUNT(sale_id) > 3; |
Code Explanation
This query aggregates sales data from the sales table by the salesman_name. It calculates the sum of sale_amount for each salesman and groups the results accordingly. The HAVING clause is used after GROUP BY to filter out those salesmen who have made more than three sales, ensuring that only those who meet this criterion are included in the output.
| Common Mistakes to Watch Out For |
|
| Follow-ups |
|
| What the Question Tests? | This question tests the candidate’s understanding of SQL aggregate functions (SUM and COUNT), the use of GROUP BY to organize data by specific criteria, and the HAVING clause for filtering aggregated results. |
10. Write a SQL query to find the month with the highest average employee attendance in a year
| Task | The goal is to write a SQL query that identifies the month with the highest average attendance of employees for a given year from the attendance table. |
| Input Format | The structure for the attendance table is as follows:
|
| Constraints |
|
| Output Format | The output should be the month (as a number or name) with the highest average daily attendance in the specified year. |
Sample Input
attendance table:
| attendance_id | employee_id | date | status |
| 1 | 1 | 2022-01-01 | Present |
| 2 | 2 | 2022-01-01 | Absent |
| 3 | 1 | 2022-02-01 | Present |
| 4 | 2 | 2022-02-01 | Present |
| 5 | 1 | 2022-03-01 | Present |
| 6 | 2 | 2022-03-01 | Present |
Sample Output
| Month | Average Attendance |
| February | 1.0 |
Suggested Answer
| SELECT
EXTRACT(MONTH FROM date) AS Month, AVG(CASE WHEN status = ‘Present’ THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS AverageAttendance FROM attendance WHERE EXTRACT(YEAR FROM date) = 2022 GROUP BY EXTRACT(MONTH FROM date) ORDER BY AverageAttendance DESC LIMIT 1; |
Code Explanation
This query calculates the average attendance for each month in the specified year (2022, in this case). It uses the EXTRACT function to get the month and year from the date, and a CASE statement within the AVG aggregate function to count ‘Present’ as 1 and ‘Absent’ as 0.
The results are grouped by month, ordered by the calculated average attendance in descending order, and limited to the top result to identify the month with the highest average attendance.
| Common Mistakes to Watch Out For |
|
| Follow-ups |
|
| What the Question Tests? | This question assesses the candidate’s ability to work with date functions (EXTRACT), conditionally aggregate data (CASE within AVG), and filter and order results based on specific criteria. |
Conclusion
Selecting the right SQL interview questions is essential for accurately assessing the technical abilities of software developer candidates. The 10 must-ask SQL interview questions outlined provide hiring managers and technical recruiters with diverse queries that test various aspects of SQL knowledge—from basic data manipulation and query optimization to complex problem-solving involving data aggregation and analysis.
These questions are designed to reveal the candidate’s proficiency with SQL syntax and analytical thinking, problem-solving capabilities, and understanding of practical applications in database management and data analysis.
For hiring managers looking to streamline their technical interview process, leveraging a platform like Interview Zen can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of candidate assessments. Interview Zen offers an intuitive environment for creating, managing, and evaluating coding interviews, enabling recruiters to focus on identifying the best talent for their team.
We invite all hiring managers and technical recruiters to take the next step in optimizing their hiring process. Sign up for Interview Zen today and start creating your technical interviews with our comprehensive guide.




